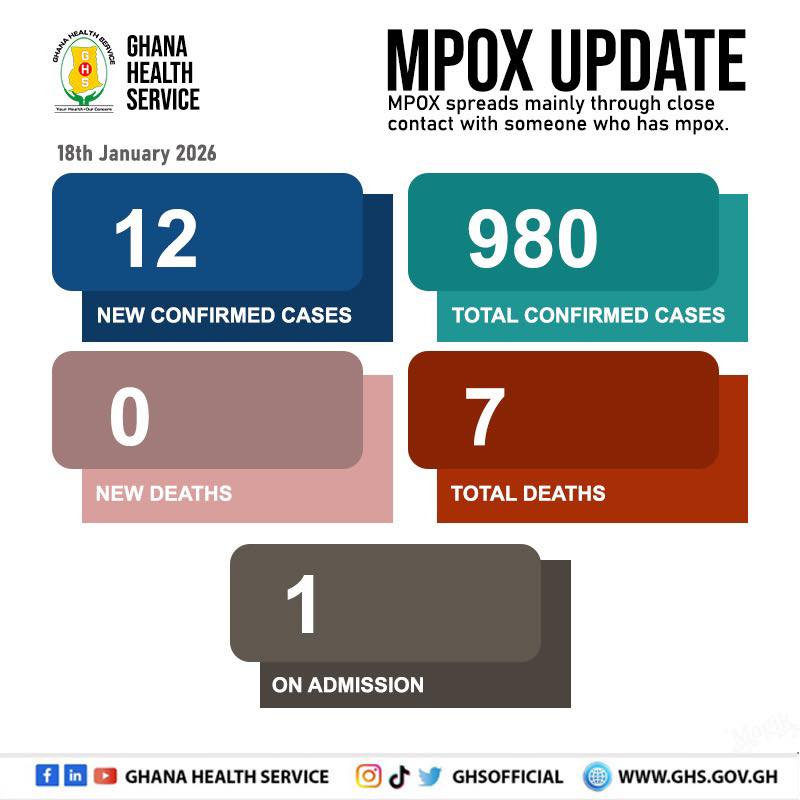
Ghana has recorded 12 new cases of Mpox, bringing the total number of confirmed infections in the country to 980 the Ghana Health Service has reported.
No new deaths have been recorded, leaving the toll at seven, and one patient remains admitted in hospital.
Mpox is primarily spread through close contact with an infected person. Health officials are urging the public to take precautions by maintaining good hygiene and seeking medical attention if they experience symptoms such as fever, rash, headache, muscle aches, swollen lymph nodes, chills, or tiredness.
Anyone noticing these symptoms is advised to visit the nearest health facility without delay.
The Ghana Health Service continues to monitor the situation closely and provides updates to help protect communities from further spread.
What is Mpox?
Mpox (formerly monkeypox) is a viral disease caused by the Monkeypox virus (MPXV), related to smallpox, causing fever, swollen lymph nodes, headache, fatigue, and a characteristic rash that progresses from bumps to blisters to scabs, typically lasting 2-4 weeks.
Transmission occurs through close contact with infected animals or people (sores, bodily fluids, contaminated items), and while often mild, it can be severe, with different viral clades (types) having varying severity. Prevention involves hygiene, avoiding contact with infected individuals/animals, vaccination, and isolation during illness, with treatments varying by severity.
Symptoms
- Early flu-like stage: Fever, intense headache, muscle aches, back pain, swollen lymph nodes, and severe fatigue.
- Skin eruption (1-4 days later): A rash that can start on the face, hands, or feet, spreading to other areas like the genitals or mouth, developing into firm, painful, pus-filled blisters that crust over and fall off.
Source: metrotvonline.com